Human vs. Non-Human Identity: The Key Differentiators
Explore the critical differences between human and non-human digital identities, revealing hidden security risks and the importance of secret detection.

Digital identities have evolved far beyond usernames and passwords for employees and customers. Behind every modern organization's firewall lurks a vast, often unmanaged population of service accounts, API keys, bots, and machine identities that outnumber human users by orders of magnitude. These non-human identities (NHIs) represent both the backbone of digital transformation and an expanding attack surface that security teams must urgently address.
Understanding Human and Non-Human Identities
Human identities represent individuals with specific roles and responsibilities within an organization. They include employees, contractors, partners, and customers who interact with systems based on their job functions or relationships with the company.
Non-human Identities encompass all digital identities not directly tied to an individual person. Here's some examples below:
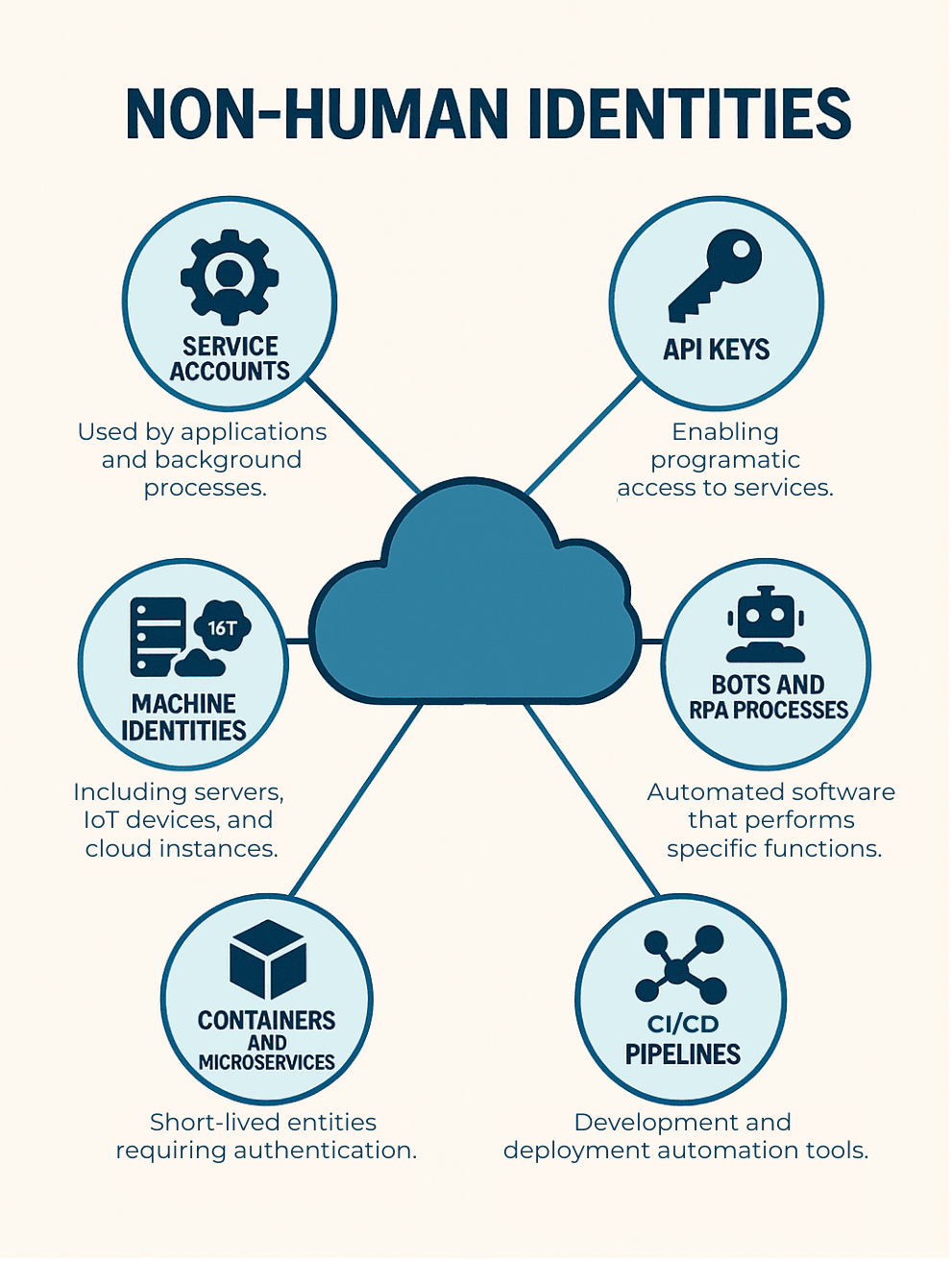
While human identities typically follow traditional Identity and Access Management (IAM) frameworks, non-human identities operate under different paradigms that require specialized security approaches. The most significant security challenges emerge not from treating each type separately, but from failing to recognize their fundamental differences.
Core Differentiators Between Human and Non-Human Identities
Operational Characteristics
Human identities are characterized by:
-
Predictable usage patterns: Typically work during business hours with consistent access needs
-
Cognitive decision-making: Can interpret contextual security factors and exercise judgment
-
Self-management capabilities: Can reset passwords, request access, and report issues
-
Limited parallel operations: Only one session or action at a time
-
Natural velocity limits: Human-speed interactions with systems
Non-Human Identities operate with:
-
Programmatic behavior: Follow defined algorithms without discretion
-
Continuous operation: Often run 24/7 without breaks
-
High-volume automation: Can execute thousands of operations per second
-
Parallel processing: Multiple simultaneous connections and actions
-
No inherent self-management: Cannot independently manage their own credentials
Authentication & Authorization Differences
Human identities authenticate through:
-
Knowledge factors: Passwords and security questions
-
Possession factors: Mobile devices, security tokens
-
Inherence factors: Biometrics (fingerprints, facial recognition)
-
Context validation: Location, device, and behavior patternsNon-human identities rely on:
Non-Human Identities rely on:
-
Embedded credentials: Hardcoded or environment variables
-
Certificate-based authentication
-
Token-based mechanisms: OAuth, JWT tokens
-
Key-based validation: API keys, encryption keys
-
IP-based restrictions: Network location validation
Risk Exposure Contrasts
Human Identities present risks through
-
Social vulnerability: Susceptibility to phishing and social engineering
-
Behavioral inconsistency: Variations in security practices
-
Privilege escalation attempts: Deliberate attempts to gain unauthorized access
-
Credential sharing: Password sharing between colleagues
-
Termination gaps: Access that persists after employment ends
Non-Human Identities create risks through:
-
Credential persistence: Long-lived, rarely changed secrets
-
Privilege concentration: Often has extensive system access
-
Invisibility: Frequently operates outside normal monitoring
-
Orphaned accounts: No clear ownership or accountability
-
Embedded secrets: Credentials stored in code or configuration files
-
Rapid exploitation potential: Once compromised, can be leveraged at machine speed
Lifecycle Management Distinctions
Human Identities Follow:
-
Structured onboarding/offboarding: Formal processes tied to employment
-
Role-based evolution: Changes aligned with job responsibilities
-
Regular certification: Periodic reviews of access rights
-
Self-service elements: Password resets and access requests
-
Clear ownership: Direct accountability for actions
Non-Human Identities Experience:
-
Ad-hoc creation: Often created outside formal processes
-
Unstable existence: May exist for minutes to months
-
Function-based access: Rights tied to technical functions, not roles
-
Unclear termination points: Often lack defined end-of-life
-
Distributed responsibility: Ambiguous ownership across teams
-
Automated provisioning: Created through CI/CD pipelines and infrastructure-as-code
Scale and Proliferation Differences
Human Identities:
-
Stable population: Growth tied to workforce expansion
-
Predictable quantity: Aligns with organizational headcount
-
Centralized management: Typically managed by HR and IT
-
Visible presence: Recorded in employee directories
-
Natural constraints: Limited by organizational size
Non-Human Identities:
-
Exponential growth: Often 45x more numerous than human identities
-
Shadow creation: Generated outside governance processes
-
Decentralized management: Created by developers, operations teams, and automated processes
-
Hidden existence: Often undocumented and untracked
-
Limited constraints: Can multiply rapidly with new technology adoption
-
Environment-specific proliferation: Multiple identities for different environments (dev/test/prod)
Monitoring Capability Differences
Human identities are monitored through:
-
Behavioral analysis: Unusual login times or locations
-
Activity thresholds: Number of actions or sessions
-
Authentication anomalies: Failed login attempts
-
Device profiling: Tracking authorized devices
-
Training effectiveness: Response to security awareness initiatives
Non-Human Identities require monitoring of:
-
Volume metrics: Unusual API call frequency
-
Resource utilization: Abnormal compute or data access
-
Permission utilization: Using dormant or rare privileges
-
Connection patterns: New or unusual connection sources
-
Execution anomalies: Deviations from expected operational patterns
-
Credential age: Identifying stale or long-lived secrets
The Critical Role of Secret Detection in Identity Security
The distinctions between human and non-human identities extend far beyond access patterns and authentication methods; they shape the very foundation of modern security strategies. While traditional identity management focuses on protecting human credentials, the explosive growth of non-human identities introduces a far greater challenge: the proliferation of embedded secrets scattered across code, infrastructure, and automation workflows.
This expanding attack surface demands a dedicated approach to secret detection. Hardcoded API keys, long-lived service account credentials, and mismanaged tokens are among the most common sources of breaches, yet they often go unnoticed until it’s too late. Consider these risks:
- Over 6 million secrets leak on GitHub annually.
- The average enterprise has thousands of exposed credentials lurking in its code repositories.
- 85% of breaches involving non-human identities originate from leaked secrets.
Without continuous, proactive secret detection, organizations risk silent but devastating compromises. Modern security solutions, like Cremit, integrate automated scanning across development environments, collaboration tools, and runtime systems to identify and remediate exposures before attackers exploit them.
Secure Your Non-Human Identities Now
NHIs outnumber human users in most environments, yet they often go unprotected. Embedded secrets in code, infrastructure, and automation workflows create serious security risks.
Start securing your secrets today with Cremit’s solution. (https://start.cremit.io) or (/contact-us) to see how Cremit helps protect non-human identities at scale.
